Climate Smart Farming Deployment Model for ERP

Photo Credit: Image by Freepik
On this page: Climate-Smart Farming Deployment leveraging a Existing-Bulk-Tariffs model - Model 11 in the ERP Project Guidelines. Read more below, or visit Strategic Guidance for Country System Assessments, Guidance for Countries in Assessing ERC Projects, or Mobilizing ERC Finance.
Project Type: Agricultural Land Management
Sector: Agriculture
Applicable Project Methodology: VM0017 Adoption of Sustainable Agricultural Land Management
The aim of this project type is to introduce sustainable land management practice activities that enhance aboveground, below-ground, and soil-based carbon stocks of agricultural areas. This helps to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reductions from agricultural practices as well as increase carbon sequestration of these areas.
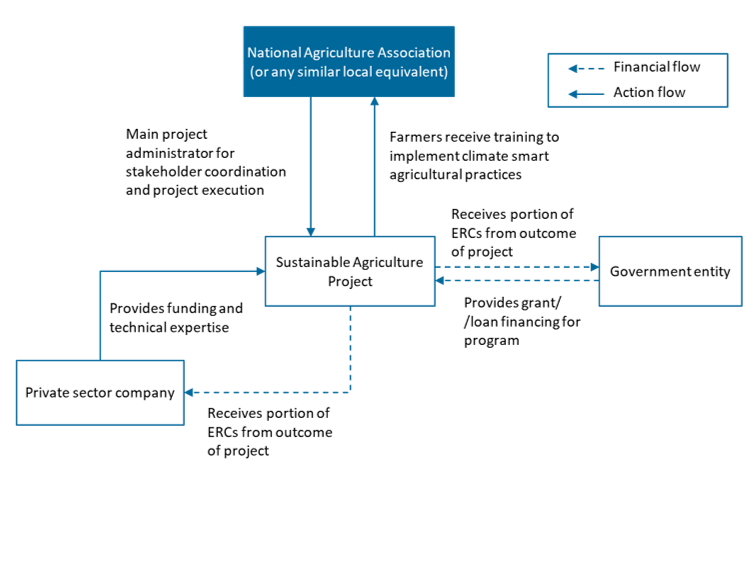
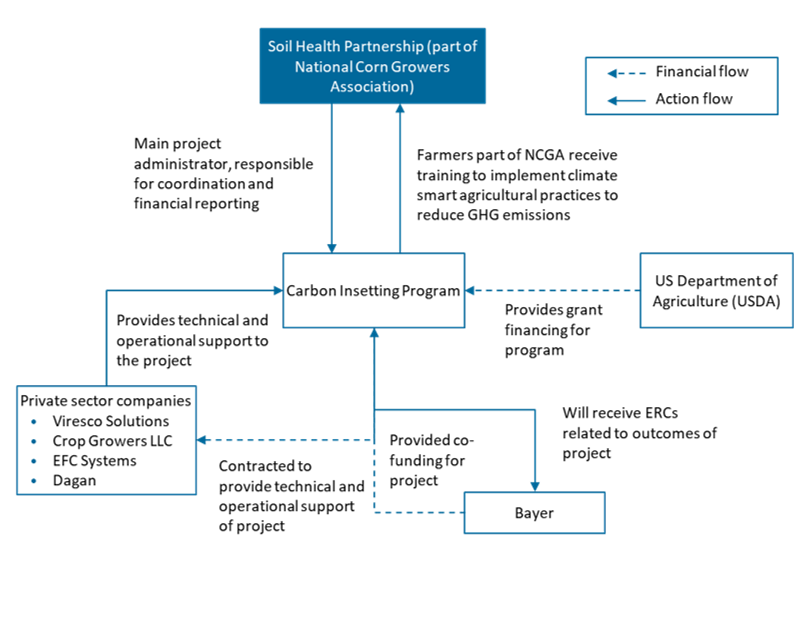
The project will be leveraging a Existing-Bulk-Tariffs model. An experienced farm operator is provided the concession to convert and transform the agricultural area by the government or state-owned entity grantor, which in turn will provide the financing to the project company for implementing climate-smart farming in said area. The grantor will be aggregating the land area for this undertaking, including the stakeholder management and permitting to ensure that the project company is able to complete its undertaking. The private sector entity will be generating revenues from the sale of emission reduction credits (ERCs), part of which may go to the government or state-owned entity for its own targets. Table 1: Model Attributes Business New This model assumes that the government or state-owned entity grantor will be granting a concession to an experienced farm operator to support the transformation of the agreed agricultural area to climate-smart farming practices. Existing Construction Build The project involves only technical and operational support Refurbish Private Funding Finance The government or state-owned entity grantor will be providing financing to the project company to undertake the activities of the firm Service Bulk Services will be provided to the government or state-owned entity grantor, in exchange for the funding provided User Service Fees Revenues in this model for the project company will be driven by the ERCs generated and sold in the voluntary carbon markets. Tariffs Proposed risk allocation of the Public Private Partnership Model Key features of PPP structure Key considerations/risks for proposed project Expected ERC end use Figure 1: Financing and Activity Flows for the Model Project description Bayer, National Corn Growers Association, and partners are developing a comprehensive intervention for corporate carbon emissions reduction with funding from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). The project focuses on promoting climate smart agricultural practices in key areas and verifies their impact, with a focus on creating management practice systems that reduce corporate emissions as well as improve economic outcomes for farmers. In this project, participating companies partnered with farmers in their supply chain who took steps to reduce their GHG emissions on their farms. Bayer has already extended this program to 16 states in the US. Targeted results No estimated annual emissions reduction available but expected socioeconomic benefits such as improved economic outcomes for farmers. Figure 2: Structure of Case Study PPP There are multiple project partners involved in this project each with a distinct role. USDA provided financing support through its Natural Resources Conservation Service’s (NRCS’s) Conservation Innovation Grants (CIG) Program. Soil Health Partnership (SHP) coordinated and reported finances for the project and used grower-cooperator sites to evaluate climate smart agriculture practices. Bayer co-funded the project and was involved in all aspects related to its GHG insetting program and reported on verified environmental benefits. Viresco Solutions provided project management, technical support, and created the carbon accounting and insetting framework, while Crop Growers LLC used Satellogic constellation data to test and develop a low-cost verification system. Dagan tested and developed another low-cost verification process using AG's Operational Tillage Information System and the DeNitrification-DeComposition (DNDC) model. EFC Systems provided precision business planning services, environmental analysis, and evaluated economic and environmental performance using precision agriculture data sources. Assuming similar case context and practices as described 'Assessing agroforestry practices and soil and water conservation for climate change adaptation in Kenya' (2020)’, The project’s Net Present Value (NPV) without ERC in- and outflows – only considering non-ERC inflows through other revenue streams or cost savings enabled by the project – is negative at $0.5 million (M)12. With ERC cashflows, the project will improve to have a positive NPV of $2.4M, demonstrating the effectiveness of ERCs to enable these types of projects. Besides that, the high upfront investments costs also necessitate finding additional revenue streams in order to justify the execution of such projects. Moreover, NPV of project may improve beyond project period as income from agricultural products recurs. Table 2: Summary of sources of inflows and outflows and key assumptions ERC revenues or inflows Average price of Agriculture project in Asia, Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) and Gold Standard (GS) Non-ERC revenues or inflows 'Assessing agroforestry practices and soil and water conservation for climate change adaptation in Kenya' (2020) Investment cost 'Assessing agroforestry practices and soil and water conservation for climate change adaptation in Kenya' (2020) Project implementation 'Assessing agroforestry practices and soil and water conservation for climate change adaptation in Kenya' (2020) ERC generation VCS Program Fees Table 3: Net cashflows summary (in USD) ERC Component Revenues/Inflows 0 33,288,634 33,288,634 Costs/Outflows -10,000 -267,909 -277,909 Net value -10,000 33,020,725 33,010,725 Primary/Non-ERC Component Revenues/Inflows 0 79,866,000 79,866,000 Costs/Outflows -13,950,000 19,890,000 5,940,000 Net value -13,950,000 99,756,000 85,806,000 Net Present Values NPV $1,769,641 NPV (ERC Component) $2,452,178 NPV (Non-ERC Component) -$527,428Proposed Structure of this Public Private Partnership (PPP) Model
Dimension
Attribute
Description

Case study: Charting A New Course – Carbon Insetting Program, USA
Summary of the model financials
Value component
Assumptions
Sources
Components
Sum of initial outlays
Sum of in- or outflows from crediting period
Total cashflow
This section is intended to be a living document and will be reviewed at regular intervals. The Guidelines have not been prepared with any specific transaction in mind and are meant to serve only as general guidance. It is therefore critical that the Guidelines be reviewed and adapted for specific transactions. Unless expressly stated otherwise, the findings, interpretations, and conclusions expressed in the Materials in this Site are those of the various authors of the Materials and are not necessarily those of The World Bank Group, its member institutions, or their respective Boards of Executive Directors or member countries. For feedback on the content of this section of the website or suggestions for links or materials that could be included, please contact the PPPLRC at ppp@worldbank.org.
Updated: June 4, 2024
TABLE OF CONTENTS
UNLOCKING GLOBAL EMISSION REDUCTION CREDIT
Guidance for Countries in Assessing ERC Projects
1. Introduction to Emission Reduction Credits
• The World Bank's Emission Reduction Program
•Classification of Emissions Reduction Credit
• Policy Context of Emissions Reduction Credit
2. Objective of the Guidance for Countries in Assessing ERC Projects
• Objective of Project Preparation Guidelines
• Introduction to the Project Assessment Framework
• Process to Conducting Assessments
• S1: Green Economy Priorities
• S3: Article 6 Readiness and Eligibility
4. Conducting the Initial Profiling and Making a Preliminary Decision
• F2: Additional Value Enabled by Project
• C1, C2, and C3: Carbon Integrity and Environmental and Social Risk Management
5. Conducting the Project Assessment and Making the Final Decision
• F1: Project ERC value and F2: Additional Value Enabled by Project
• Q2: Marketing, Sales, and Pricing
• Q3: Project Governance and Structure
• C2: Environmental Risk Management
• C3: Social Risk Management and Benefits
6. Further Guidance for Application
• Country Context-driven Factors
• Considerations for Future Scope
Abbreviations: Guidance for Countries in Assessing ERC Projects
• B: Project Assessment Template
- Model 1: MRT Energy Efficiencies Model for ERP
- Model 2: Rural Electrification Model for ERP
- Model 4: Rooftop Solar Installation Model for ERP
- Model 5: LED Streetlight Deployment Model for ERP - for Specific Technologies
- Model 6: E-bus Deployment Model for ERP
- Model 7: EV Charging Systems Installation Model for ERP
- Model 8: Biodigesters Deployment Model for ERP
- Model 9: Waste-to-Power Model for ERP
- Model 10: Waste Treatment Facility Model for ERP
- Model 11: Climate Smart Farming Deployment Model for ERP