Fund: Liveligoods Carbon Fund 3

Photo Credit: Image by Freepik
On this page: The Livelihoods Carbon Fund 3 (LCF3) launched in 2021 and combines equity capital from some international investors seeking ERC returns and others seeking financial returns to provide upfront financing for ERC activities. Read more below, or visit Strategic Guidance for Country System Assessments, Guidance for Countries in Assessing ERC Projects, or Mobilizing ERC Finance.
Issuer Livelihoods Funds Key Lessons LCF3 leverages synergies between corporates seeking secured access to a Portfolio diversification across project types and jurisdictions helps to reduce LCF3’s structure is particularly suitable for small or mid-size ERC buyers who Instrument Fund Return Depending on the type of share held (Class A, B, or The Livelihoods Carbon Fund 3 (LCF3) combines equity capital from some international investors seeking ERC returns and others seeking financial returns to provide upfront financing for ERC activities (Figure 9). Launched in 2021, LCF3 is a $150 million fund that invests in large-scale natural ecosystem restoration, agroforestry, and rural energy projects in developing countries across Africa, Asia, and Latin America. LCF3 is the third in a series of progressively larger and more impactful funds. LCF3 structures ERPAs as debt transactions with an obligation to repay in the form of ERCs. There are three types of shareholders in LCF31: LCF3’s investors comprise Bel Group, Chanel, Danone, DEG Invest, Eurofins, Global Environmental Facility, Hermès, L’Occitane Group, Mars, Mauritius Commercial Bank, McCain Foods, Orange, SAP, Schneider Electric, and Voyageurs du Monde.2 LCF3 creates synergies between the interests and preferred level of ERC market exposure of investors that want to receive ERC returns and those that want to receive financial returns, which is a key element among a package of risk mitigation elements. Portfolio diversification across project types and jurisdictions helps to reduce the overall credit risk and operational risks for LCF3 investors. Class A and Class C shareholders, mainly corporates, are exposed to ERC market risk in exchange for access to a supply of ERCs. Class B shareholders, mainly financial institutions, can tap into the increasing value of ERC markets through a diversified portfolio of ERC activities managed by an experienced impact investment fund manager but are insulated from market risk by the long-term offtake agreements and credit enhancement through a partial credit guarantee from U.S. DFC (originally agreed through USAID’s Development Credit Authority). Figure 9. Financial structure of Livelihoods Carbon Fund 3 _______________ Footnote 1: GEF, Livelihoods Carbon Fund 3 (LCF3), 2023. Footnote 2: Livelihoods Funds, The Livelihoods Carbon Funds, 2023.
FORESIGHT SUSTAINABLE FORESTRY (FSF)
source of high-quality ERCs and financial investors seeking to engage in ERC
markets with minimal risk.
the overall credit risk and operational risks for LCF3 investors, complemented
by a partial credit guarantee from U.S. DFC.
do not necessarily have the resources or expertise to engage with ERC
activities directly (e.g., extensive project and credit purchasing due diligence).
C), LCF3 investors may receive ERCs or receive
cash returns that are dependent on the sale of
ERCs through long-term offtake agreements.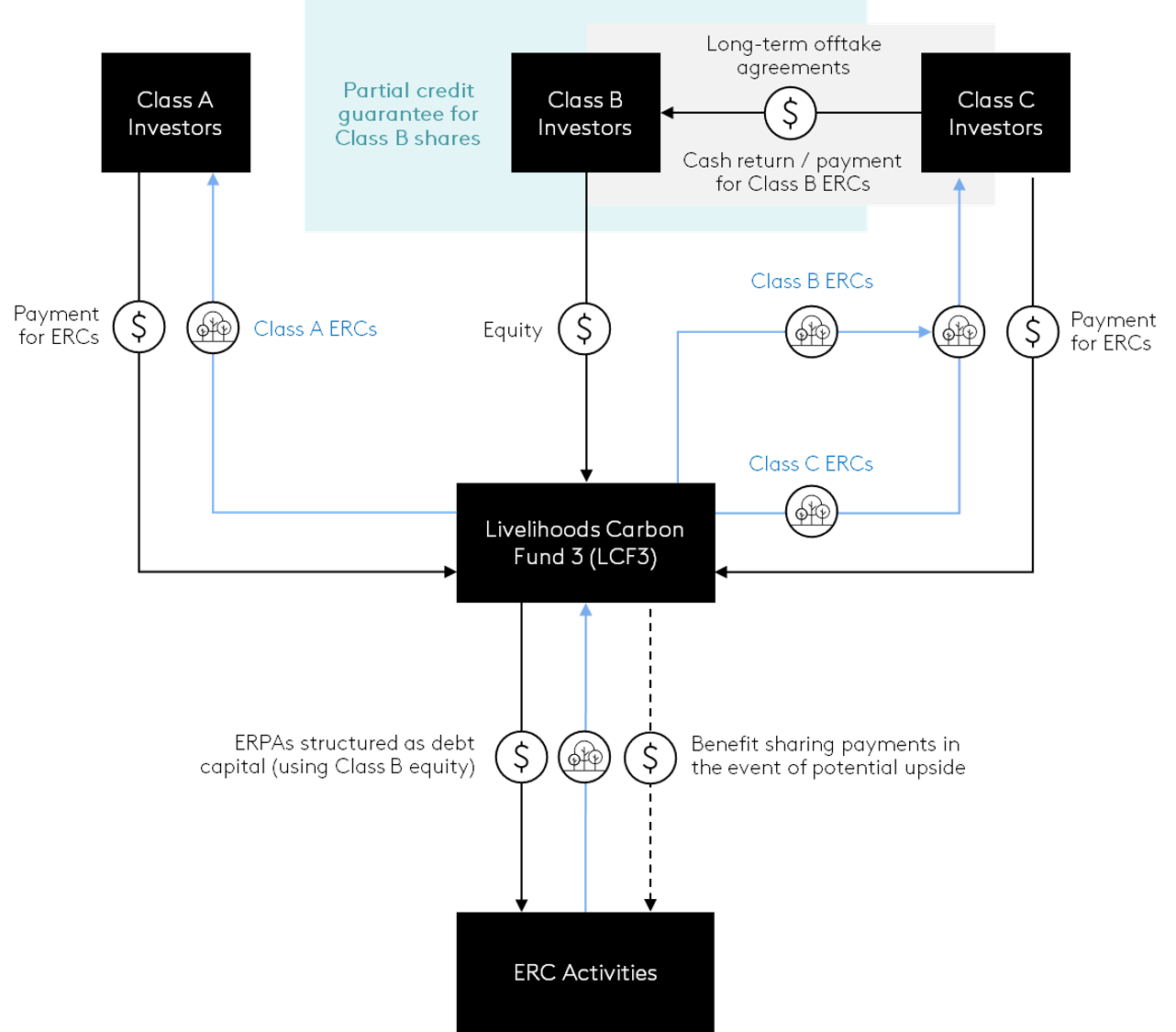
This section is intended to be a living document and will be reviewed at regular intervals. The Guidelines have not been prepared with any specific transaction in mind and are meant to serve only as general guidance. It is therefore critical that the Guidelines be reviewed and adapted for specific transactions. Unless expressly stated otherwise, the findings, interpretations, and conclusions expressed in the Materials in this Site are those of the various authors of the Materials and are not necessarily those of The World Bank Group, its member institutions, or their respective Boards of Executive Directors or member countries. For feedback on the content of this section of the website or suggestions for links or materials that could be included, please contact the PPPLRC at ppp@worldbank.org.
Updated: June 3, 2024
TABLE OF CONTENTS
UNLOCKING GLOBAL EMISSION REDUCTION CREDIT
1. Introduction to Emission Reduction Credits
• The World Bank's Emission Reduction Program
• Classification of Emissions Reduction Credit
• Policy Context of Emissions Reduction Credit
• Current Landscape of ERC Financing
• Financing structures to address key risks
• Debt: Example of Emission Reduction-Linked Bond from Vietnam
• Equity: The London Stock Exchange and Foresight Sustainable Forestry
• Fund: Liveligoods Carbon Fund 3
3. Key Enablers of ERC Finance
• Credit Risk in ERC Finance Transactions
• Political Risk for ERC Activities
• Rights to ERCs and Their Benefits
• Government Engagement and Public Sector Participation
4. Scaling Finance for ERC Generation
• Key Findings to Scale Up Private Sector Capital for ERC Activities
• Expand ERC-Backed Debt Issuance