Key Enablers of ERC Finance
Through a series of working group meetings and additional consultations with experts in the field of ERC finance, the World Bank ERP Finance Working Group identified four key risks that influence ERC transactions (Figure 10) and the most effective or promising tools or approaches for mitigating those risks. ERC generation as an economic activity and the associated technologies and practices remain unfamiliar to most financiers, and the market is still small and shallow and is fundamentally policy driven. When considering ERC activities, financiers are particularly focused on addressing credit, operational, market, and political risks. Governments, project developers, development finance institutions (DFIs), insurers, commercial financiers, and concessional financiers have a range of options to address these risks and mobilize ERC finance. This chapter highlights some of the key enablers (Table 2) to consider when structuring ERC activities and finance, because they have been demonstrably used in recent financial structures that are successfully tapping into capital markets and international investors, including those highlighted in Financing structures to address key risks, or they are enablers that potential financiers broadly acknowledge would help scale up private-sector ERC financing. While each of these enablers can be effective at addressing key risks that affect an ERC transaction, they are ultimately insufficient without the support of clear and consistent policy frameworks to guide how ERC markets are regulated. There are several efforts to further the development of these frameworks and enhance regulatory capacity, especially in emerging markets.1
Figure 10. Key ERC-related risks for financiers.
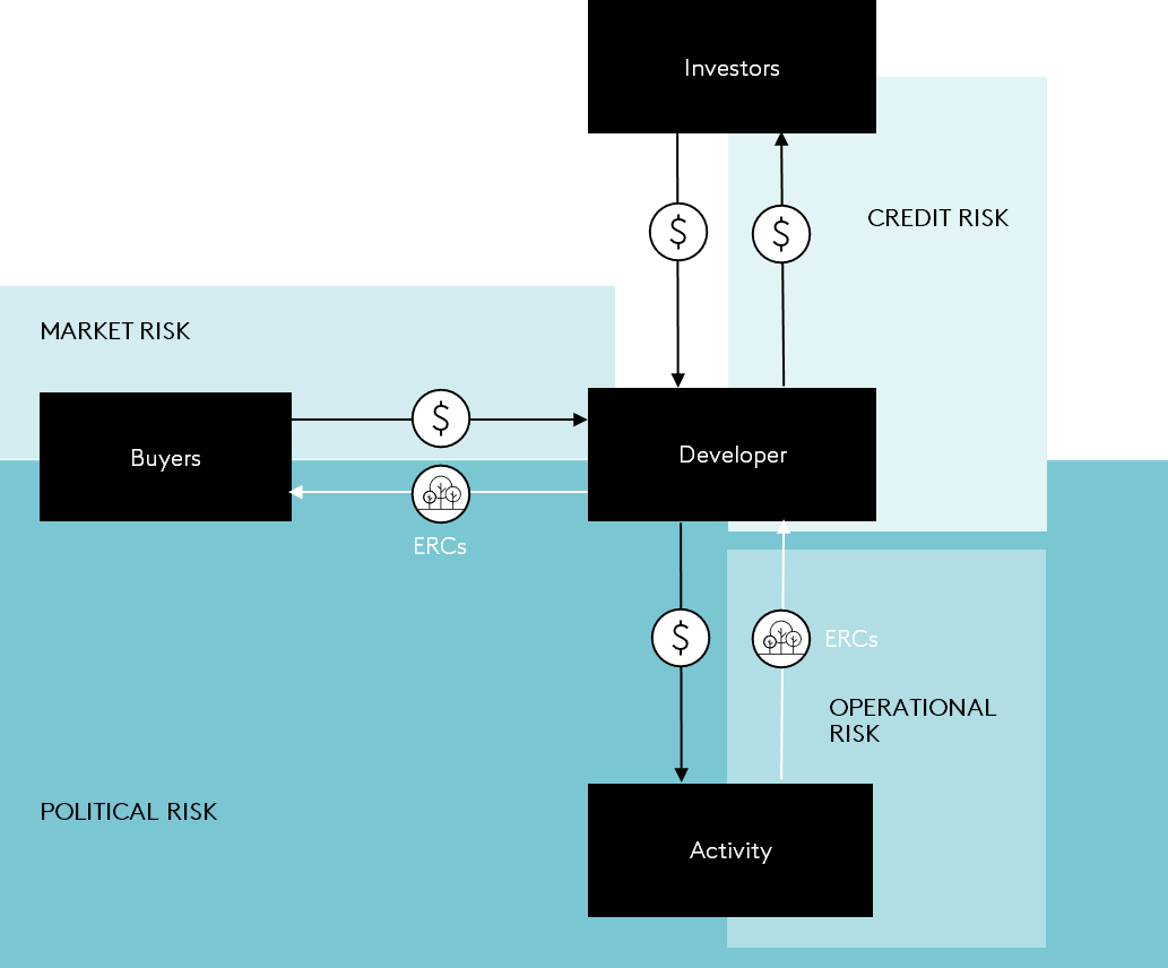
Table 2. Summary of spotlighted enablers of ERC financing, the types of risk they address, and for which case studies (ERLB, FSF, or LCF3) they were most relevant based on publicly available information.
|
Credit risk
|
Activity-level risk
|
Market risk
|
Political risk
|
|
Financial Enablers
|
Guarantees (LCF3)
Principal protection
(ERLB)
First-loss / concessional capital (LCF3)
|
|
Securing demand (LCF3)
Price support
|
DFI participation
(ERLB, LCF3)
Political risk insurance
|
|
Operational Enablers
|
|
Local stakeholder engagement (All) and benefit sharing (LCF3)
Project preparation support (LCF3) Operational insurance
|
Credit integrity (All)
|
Government engagement (ERLB)
|
|
Enabling Environmen Enablers
|
|
|
Registries (FSF)
|
Rights to ERCs and their benefits (LCF3)
Cross-border trade (ERLB, LCF3)
|
Footnote 1: See, for example, World Bank, Partnership for Market Implementation (PMI), 2023; VCMI, VCM Access Strategy Toolkit, 2023; UNDP, Carbon Payments for Development, 2023.
Sections




